The Science Behind
PLAST aims to make it easier for users wanting to apply plastic pollution assessments to find the method best suited to their needs and resources. However, to filter down the innumerable plastic pollution methodologies, data collection protocols and frameworks to a manageable number, a set of inclusion and exclusion criteria were specified, as shown below:
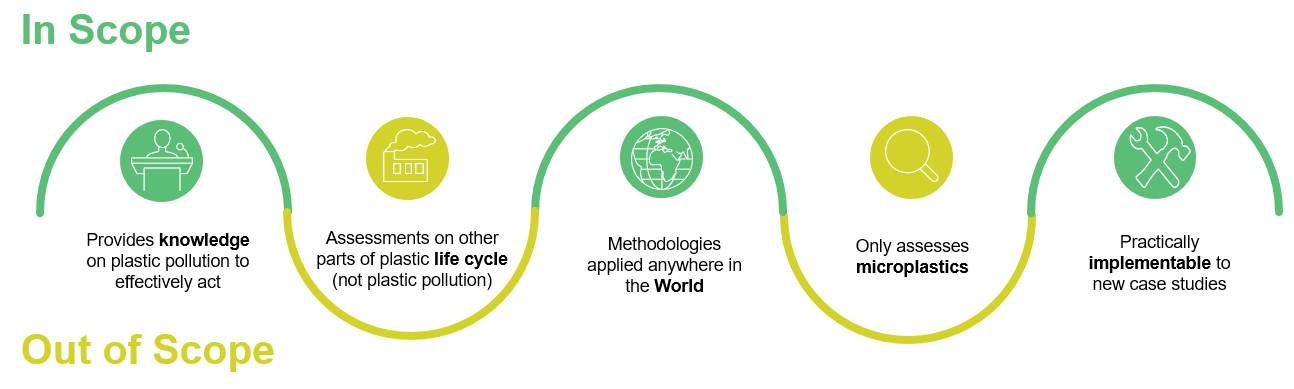
In essence, a plastic pollution assessment method is defined here as:
An implementable methodology that quantifies macroplastic pollution, providing knowledge and understanding in order to effectively act
In-scope plastic pollution assessment methodologies were categorised according to a detailed framework that assesses their primary uses, technical outputs (e.g. resolutions, scales, functionalities) and their requirements (e.g. data, time, equipment, expertise). This framework enables PLAST to match a users needs with that outputs of a methodology.
To use PLAST, users should download and install PLAST to their PC (detailed installation instructions and training can be found here). Users are then required to answers a series of questions to gauge what their overall aim and objectives are in applying plastic pollution assessments. This is split into three core parts:

Part A asks questions about the high-level objectives of a user and should be completed by someone who has an understanding of overall strategies and resources. Part B asks about the technical requirements that may exist, for example, the spatial or temporal resolution needed. Part C asks about the data currently available or available to collect as part of any plastic pollution assessment. Parts B and C should be completed by a technical user who has a good understanding of the practicalities of plastic pollution assessments.
When completing the questions, users are able to specify how important a certain feature of the methodology is. For example, a user wishing to apply a national assessment may state it is essential that the methodology is able to output results at this scale. Likewise, they may also state that understanding the flux of plastic entering oceans from rivers is important to them, but perhaps not essential.
The user specified level of importance of a assessment feature is used within the internal decision making algorithm of PLAST to suggest methodologies whereby all the essential criteria are met, and as many of the important or preferred features are also satisfied, including aspects such as data and resources. Full details of the method behind PLAST can be read in the accompanying user manual.
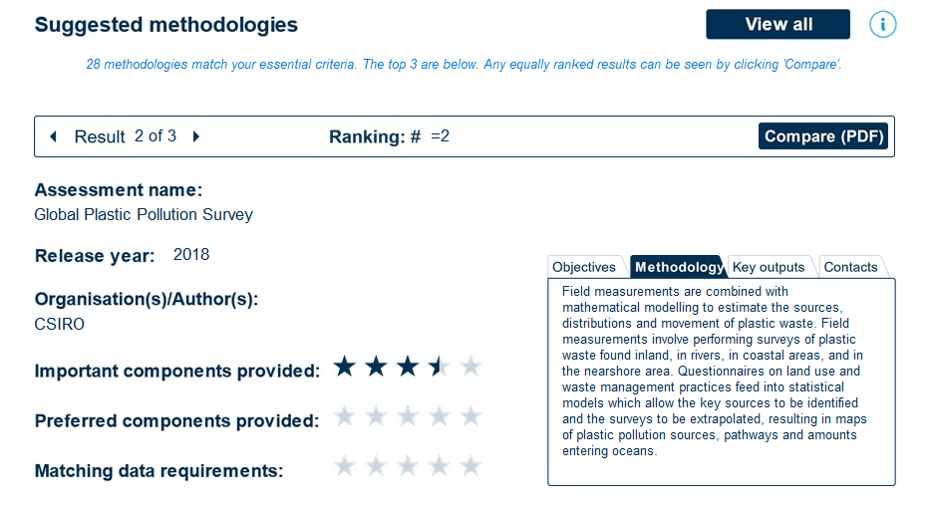
On completing the questions, PLAST shows users a list of the top 3 plastic pollution assessment methodologies that are most suitable for their needs and resources. Each suggested methodology has details of its objective, methodology, key outputs and contact details shown for it. Additionally, the user can see via a star rating system to assess how well each methodology scored against the users important and preferred features, and against data requirements.
The ranking of each of the four generalised approaches are also displayed to users in the form of a bar chart.

